PC Win Booster Online Help
Please, read our Frequently Asked Questions section first to find out answers to the most frequent questions.
PC Win Booster help in PDF Download |
PC Win Booster help in CHM |
PC Win Booster is a special utility that lets the user scan, clean and fix the Windows registry, remove obsolete, harmful or unused items from the registry and make the personal computer operate safe and fast.
Using PC Win Booster you can quickly and easily perform the following tasks:
- Remove the information that is no longer in use, left behind after incomplete uninstallation or incorrect removal of software, or used for a malware activation.
- Revert changes made to the registry if needed.
- Get rid of unnecessary temporary files created by different applications and the operating system itself.
- Delete the web browser temporary data called cache.
- Remove shortcuts that refer to invalid locations.
- Empty Recycle Bin instantly.
- Uninstall corrupted applications correctly.
- Make both registry and system backup quickly.
- Restore the Windows registry and system files to their initial status before cleanup has been done.
- Schedule which categories, when and how often should be scanned and fixed.
- Remove unused empty folders.
- Defragment disks if needed.
- Delete file duplicates.
- Fix critical errors and vulnerabilities.
- Optimize your PC.
- Strong completely uninstall programs.
- Fix process issues in RAM.
- Search and remove malware and rootkits.
To start PC Win Booster go to Start menu and choose All Programs -> Soft4Boost -> PC Win Booster -> PC Win Booster
- Introduction to the Registry
-
The registry is a system-defined database in which applications and system components store and retrieve configuration data, information and settings for all the hardware, operating system software, most non-operating system software, users, preferences of the personal computer, etc. The data stored in the registry varies according to the version of Windows used.
Note: in the latest Windows versions - Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 - the registry does not physically exist as a single file, it is a virtual entity composed of different files in the system, some of which are created during the system boot and exist only during the Windows user session and are deleted once the computer is shut down.
If there is an error in the registry, your system may not function properly. PC Win Booster helps you scan your registry for some possible problems and try and fix them to improve the overall computer performance.
Note: most of the registry changes in Windows versions require a user to have Administrator permissions to perform them; in Windows Vista and Windows 7 you will additionally need to run the program as administrator to get the full access to all the program features.
Note: it is not recommended to edit the registry data unless it is absolutely necessary, that is your computer experiences slow performance issues, some programs behave inadequately and so on. Please make sure you create a backup each time you scan and fix some registry problems.
The registry contains the following root hives:
• HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR) - stores information about the system registered applications, such as file extensions tying them to the applications used to handle these extensions. In fact this hive combines data from the HKLM\Software\Classes and HKEY_USERS\Current_User's_SID_Classes registry sections.
• HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU) - stores settings that are specific to the currently logged-in user.
• HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) - stores settings that are general to all users on the computer - information about system hardware drivers, services, software and Windows settings.
• HKEY_USERS (HKU) - contains subkeys corresponding to the HKEY_CURRENT_USER keys for each user profile actively loaded on the machine, though user hives are usually only loaded for currently logged-in users.
• HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG - contains information gathered at runtime; information stored in this key is not permanently stored on disk, but rather regenerated at the boot time.
Below is the list of registry sections, which are scanned by PC Win Booster:
• COM/ActiveX - registry section in which the COM-servers used by various applications are registered (in-process servers (.dll files) or out-of-process servers (.exe files)). The program scans for the .dll or .exe links in the registry that point to the nonexistent files on the computer hard disk drive. A COM-server can also link to a type library (usually a .tlb-file) that does not exist. In case the DefaultIcon registry subkey is present in the category, the program will also scan for the presence or absence of the file containing the file icons.
• Application Paths - registry section used to store the full paths to the applications launched using the Run window or command prompt. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the applications and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Uninstall Entries - registry section used for programs installation/deinstallation paths entries. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the applications installer/uninstaller files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• File Extensions - registry section used to store the full paths to the applications, file icons and additional commands associated with the file extensions. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the applications and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Windows Fonts - registry section used to store the full paths to the Windows fonts or the font file name (in this case the font file must be present in the \Windows\Fonts\ directory). The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the font files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Help Files - registry section used to store the full paths to the Windows programs helps. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the helps files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Internet Explorer typed URLs - registry section used to store the history of the URL-addresses typed in the Internet Explorer address bar. The program scans for the presence of these entries.
• Explorer MRU list - registry section used to store the history of the entered Run window commands, recent documents list, last visited pages and opened and saved files. The program scans for the presence of these entries.
• Search Assistant MRU list - registry section used to store the history of the entered Search window commands. The program scans for the presence of these entries.
• Media MRU list - registry section used to store the history of the latest media files played by the Windows Media Player. The program scans for the presence of these entries.
• Shared DLLs - registry section used to store the full paths to the library files (DLLs) that can be used by several programs. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Sounds and App Events - registry section used to store the full paths to the Windows sound files used by various applications. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the sound files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Windows Startup - registry section used to store the full paths to the applications which are executed automatically during the system startup. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Windows Applications - registry section used for programs installed on PC. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• MRU Cache - registry section used to store the history of the entered applications. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
• Invalid Firewall Settings - registry section used to store the list of authorized applications for Windows Firewall. The program scans for the nonexistent paths to the files and deletes the entries if these files could not be found.
Note: PC Win Booster searches not only the HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry hive, but also the HKEY_USERS that store data for all the users on the computer. Please make sure you do backup your windows registry before you fix the existing problems.
[Back to the top]
-
- Introduction to the Defragmentation
-
Defragmentation is the process of locating the noncontiguous fragments of data into which a computer file may be divided as it is stored on a hard disk, and rearranging the fragments and restoring them into fewer fragments or into the whole file. Defragmentation reduces data access time and allows storage to be used more efficiently. Some operating systems automatically defragment storage periodically; others require that the user occasionally use a special utility for this purpose.
Defragmentation is advantageous and relevant to file systems on electromechanical disk drives. The movement of the hard drive's read/write heads over different areas of the disk when accessing fragmented files is slower, compared to accessing the entire contents of a non-fragmented file sequentially without moving the read/write heads to seek other fragments.
A common strategy to optimize defragmentation and to reduce the impact of fragmentation is to partition the hard disk(s) in a way that separates partitions of the file system that experience many more reads than writes from the more volatile zones where files are created and deleted frequently. The directories that contain the users' profiles are modified constantly (especially with the Temp directory and web browser cache creating thousands of files that are deleted in a few days). If files from user profiles are held on a dedicated partition, the defragmenter runs better since it does not need to deal with all the static files from other directories. For partitions with relatively little write activity, defragmentation performance greatly improves after the first defragmentation, since the defragmenter will need to defrag only a small number of new files in the future.
Note: PC Win Booster scans local drives and makes decisions, whether defragmentation is needed to the each local drive.
Note: Defragmentationis is a very long time process so in PC Win Booster there is settings “shutdown the computer after fixing”.
[Back to the top]
-
- Program Interface
-
PC Win Booster interface is quite simple to use and lets the user perform all the actions with a few mouse clicks. The program Main Window looks the following way:
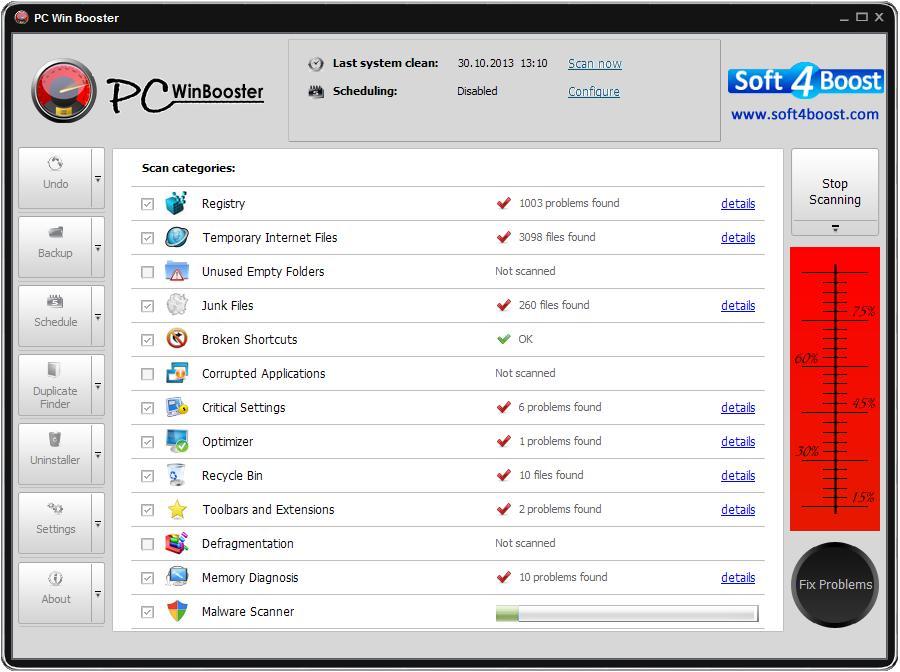

Use this button to revert the registry to the state it was in before last cleans.

Use this button to create both registry and system backups to restore from them later.

Use this button to open the Duplicate Finder window to search file duplicates.

Use this button to open the Uninstaller window to remove installing programs.

Use this button to create a cleanup schedule so that the program could scan and fix your system automatically at the appointed time.

Use this button to open the Settings window to change the program settings.

Use this button to open the About the Program window displaying the information on the program current version and the end-user license agreement.
The Status Area lets the user see date and time when the last scanning and fixing were made and know whether scheduling is enabled or not.
The Category/Result Area initially contains the list of available categories to scan within. It also displays the found problems in details if the scanning has been performed.
[Back to the top]
-
- Scanning and Fixing: Overview
-
The scanning is a fully automated process. This means that the program will do everything itself. But before scanning you should choose categories that will be included into the scan process. Available categories are:
Registry
Temporary Internet Files
Unused Empty Folders
Junk Files
Broken Shortcuts
Corrupted ApplicationsCritical Settings
Optimizer
Recycle Bin
DefragmentationMemory Diagnosis
Malware Scanner
After choosing the categories to scan, click the Start Scanning button to initiate the scan process. Once the scanning is over, a result of the found problems will be displayed in the Category/Result area. To fix the found problems, click the Fix Problem

Note: objects currently scanned within a category are shown in the left bottom corner of the Main Window
-
- Creating Backup and Using the Restoring: Overview
-

Regular backups will prevent your system and its registry from data loss and will let you return to the saved state whenever needed.
To create a backup, click the Backup button on the Menu Panel, the following window will appear:

You can create two types of backups through the Backup window:
Registry Backup
System BackupNote: when you launch PC Win Booster for the first time you will be offered to make the system backup at once. The system backup under the name "PC Win Booster First Launch" will be created if you accept to do that.
Registry Backup
The registry backup lets create the backup copy of the registry in whole. To create a registry backup, click the Registry Backup button:

Note: you can specify your backup name in case the default name on the current date seems to be uninformative for you.
The registry backup process will start. It takes some time to complete:

When the registry backup is completed the message box informing of the successful completion will appear:

To restore from a registry backup, select it in the table and then click Restore. The restore process takes some time to complete:

When the registry restore process is completed your computer will be restarted for rollback to take effect:

To delete a registry backup , select it then click the Delete item from the right-click menu.
Note: the System Backup requires the Windows System Restore feature enabled. Please, make sure it is enabled otherwise creating the registry backup will be available only: Start -> Control Panel -> System -> System Protection and select disks on which system restore points should be created. Make sure you use the Classic View for the Control Panel to see the System icon.
To create a system backup, click the System Backup button:

Note: you can specify your backup name in case the default name on the current date seems to be uninformative for you.
Note: you might see some system restore points listed although you did not create them before, those are points created by Windows.
The system backup process will start. It takes some time to complete:

When the system backup is completed the message box informing of the successful completion will appear:

To restore from a system backup, select it in the table and then click Restore. The restore process takes some time to complete:

When the system restore process is completed, your computer will be restarted for rollback to take effect:

Note: you can not delete the system backups, use the operating system options to do that.
-
- Using the Scheduling
-
If you want to automate the work of PC Win Booster and let it perform cleaning on chosen categories once, say, a week and at a certain time, you should use the Schedule feature.

To use the Schedule feature, click the Schedule button on the Menu Panel and check the Enable Scheduling option in the window that appears:

Scan categories - use this option to check the categories that should be included into the clean on schedule.
Recur every - use this option to set how often the clean on schedule should be performed.
Start time - use this option to set an exact time (hours:minutes:seconds) when the clean on schedule should start.
To open the folder containing reports made on the results of the scheduled cleans, click the Show Reports button.
Note: if the folder is empty, the Show Reports button is disabled.
Note: if the scheduled time has come but PC Win Booster is unloaded, you will see the "Clean on Schedule" notification in the system tray and cleanup will start automatically.
-
- Changing the Program Settings
-

To change the default program settings, click the Settings button on the Menu Panel.
The General tab

Application settings
Run scanning on application launch - use this option to perform the scanning automatically each time PC Win Booster is loaded.
Show scan results before fixing - use this option to avoid the auto fixing of the found problems and see the results of scanning to have the opportunity to choose which problems exactly should be fixed.
Shutdown computer after fixing - use this option to shutdown PC after fixing will be completed.
Create system restore point before fixing - use this option to create a system restore point each time before fixing is performed.
Log application and its components behavior - use this option to journalize the PC Win Booster internal mechanism behavior including the work of its components. Sending such reports to us helps make the future releases of PC Win Booster even much better.Select an operation - use this option to choose what should be done with the found temporary internet/junk files and broken shortcuts:
Move to Recycle Bin
Permanently deleteSelect a skin style - use this option to choose PC Win Booster skin style.
The Registry tab

Registry category settings - use this option to choose which registry sections will be included into the scanning.
Ignore list - use this option to define which registry keys will be excluded from scanning. It is useful when you consider that a found problem does not have an effect on your system that much and want to decrease the general scan time. To delete a key or all the keys from the Ignore List use the right-click menu.
Note: to add the registry keys to the ignore list, scan the registry for problems first then click the details link to see the found problems and use the right-click menu Add to Ignore List item for a selected key.
The Junk files tab

Clean My Recent Documents - use this option to scan for the recently used items.
Clean temporary files - use this option to scan for temporary files on system hard drive.
Clean Print Hood - use this option to scan for temporary files on Print Hood folder.
Clean system junk files - use this option to scan for junk files in Windows system folder.
Clean applications junk files - use this option to scan for some applications junk files (such as Adobe Flash Player, Oracle Java and etc. in case they are installed on your computer).
Clean Net Hood - use this option to scan for temporary files on Net Hood folder.
Clean by junk file extensions - use this option to enable the list of extensions to scan for junk files by them.
Clean Thumbnail Cache - use this option to enable the list of local drives to scan .db files.
Scan path - use this option to define on which local hard drives to scan for junk files by extension or .db files.
Junk file extensions - the list of available junk file extensions.The Temporary Internet files tab

Clean cache - use this option to scan for the browsers cache data installed on PC.
Clean History - use this option to scan for the browsers history data installed on PC.
Clean Cookies - use this option to scan for the browsers cookies data installed on PC.
The Empty Folders tab

Scan path - use this option to define on which local hard drives to scan for junk unused empty folders.
The Defragmentation tab

Scan Settings - use this option to choose what should be analyze for defragmentation:
Analyze Only
Analyze and Move Clusters
Analyze and Sort ClustersDefragmentation Settings - use this option to choose what should be defragment with the fragmented local drives:
Defragment Only
Defragment and fast Optimize
Defragment and fully OptimizeScan path - use this option to define on which local hard drives to check for fragmented items.
-
